Inspire AI and Bring Your Ideas to Life!
The world of artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly expanding, with new advancements being made every day. One exciting area of AI is Generative AI, which involves using algorithms to create original and innovative content. However, creating effective prompts is a critical component of developing Generative AI that inspires users and brings their ideas to life. In this article, we will explore different taxonomies of prompts used in natural language processing (NLP) and other areas of AI. By understanding these taxonomies, developers can create prompts that generate more accurate and relevant responses based on the user’s intent and goals.
Yes, there are taxonomies of prompts that are commonly used in natural language processing (NLP) and other areas of artificial intelligence (AI). These taxonomies are used to classify prompts based on their structure, content, and purpose. Here are some examples:
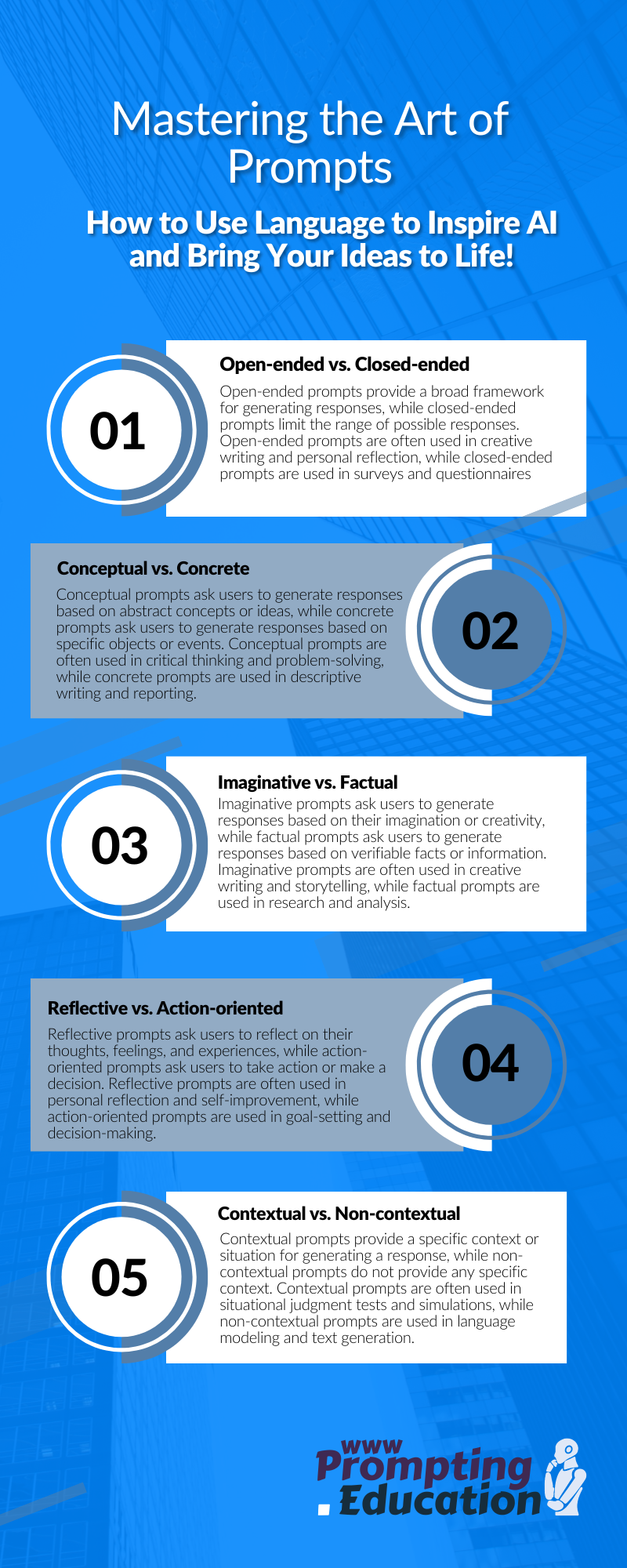
Prompts Open-ended vs. Closed-ended:
Open-ended prompts provide a broad framework for generating responses, while closed-ended prompts limit the range of possible responses. Open-ended prompts are often used in creative writing and personal reflection, while closed-ended prompts are used in surveys and questionnaires
Conceptual vs. Concrete:
Conceptual prompts ask users to generate responses based on abstract concepts or ideas, while concrete prompts ask users to generate responses based on specific objects or events. Conceptual prompts are often used in critical thinking and problem-solving, while concrete prompts are used in descriptive writing and reporting
Imaginative vs. Factual:
Imaginative prompts ask users to generate responses based on their imagination or creativity, while factual prompts ask users to generate responses based on verifiable facts or information. Imaginative prompts are often used in creative writing and storytelling, while factual prompts are used in research and analysis.
Reflective vs. Action-oriented:
Reflective prompts ask users to reflect on their thoughts, feelings, and experiences, while action-oriented prompts ask users to take action or make a decision. Reflective prompts are often used in personal reflection and self-improvement, while action-oriented prompts are used in goal-setting and decision-making.
Contextual vs. Non-contextual:
Contextual prompts provide a specific context or situation for generating a response, while non-contextual prompts do not provide any specific context. Contextual prompts are often used in situational judgment tests and simulations, while non-contextual prompts are used in language modeling and text generation.
These taxonomies of prompts can be helpful in designing Generative AI programs that generate more accurate and relevant responses based on the user’s intent and goals. By understanding the different types of prompts and their purposes, developers can create prompts that align with the user’s needs and generate more meaningful output.
In conclusion, the taxonomies of prompts in NLP and AI can help developers create Generative AI that inspires users and brings their ideas to life. Open-ended vs. closed-ended, conceptual vs. concrete, imaginative vs. factual, reflective vs. action-oriented, and contextual vs. non-contextual prompts all play a crucial role in creating an engaging user experience. By incorporating these different types of prompts into your design, you can create Generative AI programs that accurately reflect the user’s intent and generate more meaningful output.
So go ahead, embrace the power of AI, and bring your ideas to life with effective prompts!











0 Comments